Page 24 - The Beauty and Sorrow in Endodontics-Prologue
P. 24
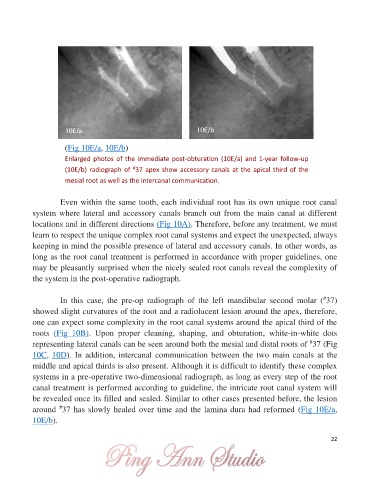
10E/a 10E/b
(Fig 10E/a, 10E/b)
Enlarged photos of the immediate post-obturation (10E/a) and 1-year follow-up
(10E/b) radiograph of 37 apex show accessory canals at the apical third of the
#
mesial root as well as the intercanal communication.
Even within the same tooth, each individual root has its own unique root canal
system where lateral and accessory canals branch out from the main canal at different
locations and in different directions (Fig 10A). Therefore, before any treatment, we must
learn to respect the unique complex root canal systems and expect the unexpected, always
keeping in mind the possible presence of lateral and accessory canals. In other words, as
long as the root canal treatment is performed in accordance with proper guidelines, one
may be pleasantly surprised when the nicely sealed root canals reveal the complexity of
the system in the post-operative radiograph.
#
In this case, the pre-op radiograph of the left mandibular second molar ( 37)
showed slight curvatures of the root and a radiolucent lesion around the apex, therefore,
one can expect some complexity in the root canal systems around the apical third of the
roots (Fig 10B). Upon proper cleaning, shaping, and obturation, white-in-white dots
#
representing lateral canals can be seen around both the mesial and distal roots of 37 (Fig
10C, 10D). In addition, intercanal communication between the two main canals at the
middle and apical thirds is also present. Although it is difficult to identify these complex
systems in a pre-operative two-dimensional radiograph, as long as every step of the root
canal treatment is performed according to guideline, the intricate root canal system will
be revealed once its filled and sealed. Similar to other cases presented before, the lesion
#
around 37 has slowly healed over time and the lamina dura had reformed (Fig 10E/a,
10E/b).
22